Learning Outcomes in Listing:
i. Understand the role of oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions in biological energy transfer.
ii. Recognize the importance of redox reactions in processes like photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
iii. Identify how redox reactions contribute to the energy efficiency of cells.
Learning Outcomes Described:
In this lesson, students will unravel the significance of redox reactions as a fundamental mechanism for energy flow in living systems. They will learn that these reactions involve the transfer of electrons between molecules, thereby facilitating the conversion of energy from one form to another, essential for metabolic processes. Understanding redox reactions is key to comprehending how cells harness and utilize energy to fuel life's activities.
Summary of Lesson:
Oxidation-reduction reactions are central to the metabolic processes that power life. They involve the transfer of electrons and the flow of energy through living systems, providing the necessary force for biological functions such as muscle contraction, nerve conduction, and biosynthesis.
i. The Basics of Redox Reactions:
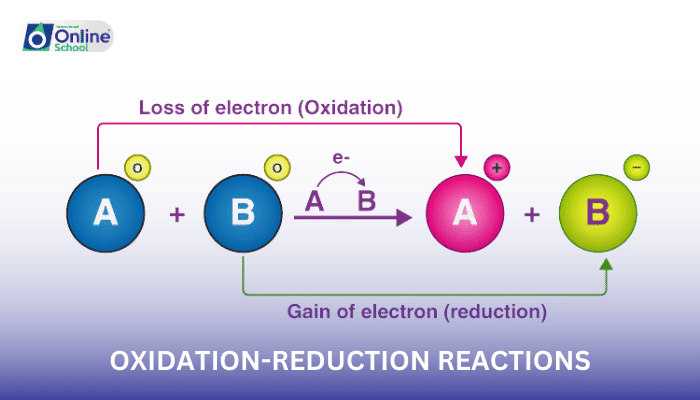
In redox reactions, oxidation refers to the loss of electrons, while reduction refers to the gain of electrons. The substance that donates electrons is oxidized, and the one that accepts electrons is reduced.
These reactions are crucial in cellular respiration, where glucose is oxidized to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of ATP.
ii. Energy Transfer in Cells:
The energy released during oxidation is not lost but transferred to molecules like NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide), which is reduced to NADH, a temporary energy carrier in cells.
In photosynthesis, light energy drives the reduction of carbon dioxide to form glucose, storing energy in chemical bonds.
iii. Efficiency of Redox Reactions:
Redox reactions are stepwise, allowing cells to extract and store energy efficiently. They prevent the loss of energy as heat and enable its capture in a usable form.
List of Important Questions for Self-Study:
i. What is the significance of electron transfer in redox reactions?
ii. How do redox reactions contribute to the generation of ATP?
iii. Why are redox reactions considered reversible?
iv. How do redox reactions in photosynthesis differ from those in cellular respiration?
v. What role do electron carriers like NAD+ play in redox reactions?
Important Terminologies Used in Lesson:
i. Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions: Chemical reactions that involve the transfer of electrons between two species.
ii. Oxidation: The loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.
iii. Reduction: The gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.
iv. NAD+/NADH: Electron carriers that play a critical role in energy metabolism.